Sky Charts
Configuring the appearance of objects
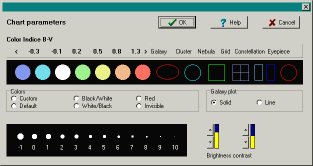
This panel allows you to change the appearance of the stars and nebulae.
The first section gives you the option of changing the colors of the
stars and nebulae according to their B-V color index, the background color
and the coordinate grids.
Click on the corresponding element to change its color.
The section "Color" gives you the option to choose the appearance,
in color, black and white, or in red. The selection "invisible" means that
only the image with the labels but without the objects are displayed. If
you want to switch to night vision you have to change the color of the
window as well. You can do that by first running the file "schemesnuit.reg"
and then choose "NuitRouge" as the appearance model of the display parameters.
The section "Galaxy Plot" lets you choose between a fill in or a border-line
selection. Select "Solid" when you work on the screen or when printing
to a color printer and select "Line" when you print to laser or impact
printers. This selection is preferable also if you want to draw on a picture.
The last selection lets you adjust the size of the stars according
to their magnitude. Use the buttons brightness +/- and contrast +/- to
alter the absolute or relative size of the stars.
Label of the objects
It is possible to assign a label to the type of object that has been selected.
If the option "Display" is checked, then a label is given for all selected objects.
The option "Options" lets you choose the information you want to display (name, magnitude, coordinates), where the information is displayed (left or right), the label text color and size, and the type of object that has to be displayed.
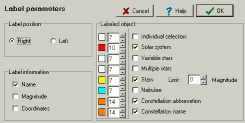
The choice "Individual Selection" means that only the selected objects
will be given a permanent label until you remove them with the option "Clear
Selection".
In the case of stars it is possible to assign a label only to those
objects that are at least a certain value brighter than the faintest star
currently displayed on the chart.
Date and Time
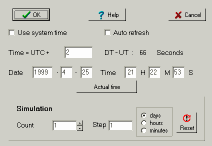
Define the date and time used to calculate the position of the planets, comets, asteroids as well as the azimuth position and the proper motion.
It is possible to use the system date and time or you can enter any valid date and time between year -3000 and +3000.
If the option "Auto Refresh" has been selected, then the time is updated every minute, otherwise the default time is when the program was started and will be used throughout the session ( unless you manually refresh it with the button "Actual time").
The time zone has to be given relative to UTC. Give the difference in hours to obtain your local time: this number is positive if you are located east of Greenwich and negative if you are located west of it.
The difference between the dynamic time used by the program and the standard time is given.
Simulation :
It is possible to calculate an objects position for several dates.
Give the number of dates you would like and the interval between them.
Observatory
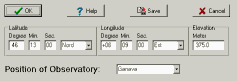
Define the location of the observation site to be used when calculating the parallax and the azimuth position.
Enter the latitude, the longitude and the altitude (in metres) of your observatory.
You can assign a name to a location. Press "Save" to keep it for next session. It will appear in the list of the available locations.
Projection types

This panel lets you choose the projection you want to be used when displaying
a chart according to the selected field width. Not all the projections
can be used in any case. I.e. the tangent projection has a great distortion
for fields larger than 45° and diverge for 90°. The sinus projection
overlaps at more than 90°.
The available projections are:
- ARC : Arc length. It is the default projection up to 180°. It corresponds to the projection of a Schmidt camera.
- TAN : Tangent. It corresponds to the projection of a picture obtained with a telescope or a photographic lens.
- SIN : Sinus. Used to display images in radio-astronomy.
- CAR : Cartesian. The default projection between 180° and 360°. It is not of great interest apart from the fact that it can display very large fields of vision.
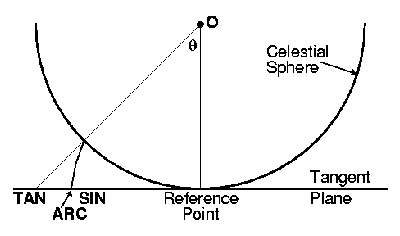
by E. Griessen, AIPS memo 27
The selected projection described up to here can be modified according
to the header of the file in FITS format containing WCS when you load such
an image.
Displaying images
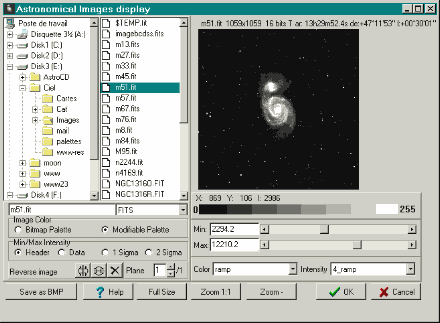
This panel lets you select the image that will be displayed together with the chart.
The image is loaded in a preview window. You can modify the display
tresholds (min and max), the color palette (composite colors LUT and intensity
tables ITT) and zoom a portion of the image.
It is also possible to display the image in its original dimension
and then zoom it by using the + and - keys.
In the case of FITS format files, which contain the coordinates RA, DE or GLAT, GLON (i.e. the images provided from DSS-ESO or IRAS) the program uses the coordinates and the projection from the header of the FITS format to automatically positioned to the current chart. Please notice that it is only possible to zoom a section of the image from the preview window and not on the main screen, otherwise the automatic positioning does not work. In the case of other image formats it is necessary to place the image on the chart manually. You can of course use the function "Online Resources "to download an image directly from the Internet.
It is possible to derive the initial thresholds from the information
contained in the file header, from the lowest and highest values or from
the average plus one or two standard deviation values.
If the image file contains more than one plane (NAXIS3 > 1) you can
select between them with the option "Plane".
In the case that the sequence of the pixels is not standard you can
mirror the image with the option "Reverse Image".
You may also apply a convolution filter to the image. Only pixels with
a value bellow treshold are filtred.
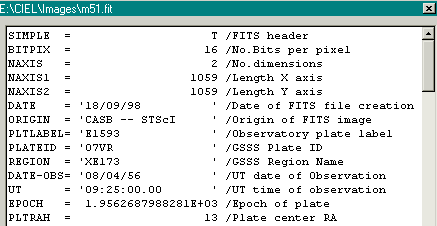
The right mouse button on a file name displays the header of the file in the format FITS or PIC.
In the case of bitmap formats its is possible to check the option "Bitmap Palette" from the selection box "Image Color". In this case all the other functions are disabled. Otherwise and if the image is a 24 bit format, the program generates a gray level from the average of all the RGB planes (plane=0) or each color independently (plane=1,2,3). In both cases the image can be modify as for the files in format FITS or PIC.
You can save the current image in a file in BMP format and reuse it later with the same appearance.
The following formats are supported:
FITS integer 8,16,32 bits, real
32,64 bits *.fit *.fts *.fits
PIC (MIPS) integer 16 bits
*.pic
Bitmap 8,24 bits *.bmp *.dib
JPEG *.jpg *.jpeg (not progressive)
GIF *.gif (not progressive)
TGA *.tga
RLE *.rle
PCX *.pcx
With the OK button you load the image into the current chart.

Note regarding the coordinates of the FITS files:
There unfortunately is not a unique and standardized way of describing
the WCS in a FITS file. This program support the three most common methods
: CROTA2, CDi_j, PCiiijjj.
It has been tested with many files obtained from different sources.
It is however impossible to guarantee that a particular file has not implemented
a variation of this format. In this case an error would certainly arise.
If you are not certain of the format of an image please consult the comments
in the header of the file.
Bulk calculation of asteroids
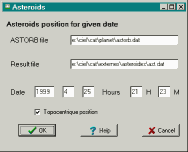
This function computes the position of all asteroids for a given date.
Please enter the complete path to the file "astorb.dat" and of the
resulting file, the date and time of the observation and if the position
has to consider the topocentric parallax.
It is advisable to keep the original values for the names of the files.
The update of astorb.dat is available using the "Online
Resources" option.
To display the position of the asteroids on the chart you have to use
the option "External Catalogues", either according to the magnitude or
to the size of a symbol. These definitions are available in "default.opt".
On a Pentium 166 it takes 40 seconds to calculate the position of 40,000
asteroids.
Warning !
The original astorb.dat file is in UNIX format (end-of-line = LF).
You must convert it to the DOS format (end-of-line = CR+LF) before you
can use it with "Sky Charts". This done automaticaly if you use the "Online
Resources" option to load the file.
Online Resources
This menu gets you directly to the Internet resources.
You have to be connected to the Internet before you can use this function.
If you want more information on the home pages themselves, just click
on the information URL.
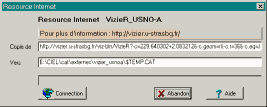
The following resources are available:
Images corresponding to displayed chart:
- SkyView : Images in all wave lengths
- ESO Skycat Digitized Sky Survey : Palomar atlas for the whole sky. The image dimension is limited to 1600 square minutes. The size of the corresponding file is 2.5 KB multiplied by the square size in minutes.
- ESO Skycat Digitized Sky Survey 2 : The same survey but with a 15 micron scan ratter than 25 micron. The pixel resolution is 1 arcsec instead of 1.7 arcsec. The files are three time bigger.
Extraction of large star catalogs:
The data requested from these catalogs corresponding to the current chart is stored in a temporary file and automatically defined as catalog according to the magnitude, the disabling is done in this panel.
HST Guide Star Catalog (20,000,000 stars)
- CDS VizieR : Stars up to the magnitude 15. The field is limited to 5 degrees or 5000 stars.
- ESO Skycat : Stars up to magnitude
15. The field is limited to 2 degrees or 1000 stars.
USNO-A (526,000,000 stars)
- CDS Vizier : USNO-A2.0 Stars up to magnitude 20. The field is limited to 2 degrees or 5000 stars.
- ESO Skycat : USNO-A1.0 Stars up to magnitude 20. The field is limited to 2 degrees or 5000 stars.
Comets and asteroids
Data from CBAT/MPC
:
- Update of the currently visible comets. If a file CAT\PLANET\COMETES.OLD exists, then this file is appended to the transferred file. This feature lets you keep old elements originating from previous observations.
- Update of the bright asteroid list at opposition during the current year.
- Update the asteroid list from ASTORB data base to file CAT\PLANET\ASTORB.DAT. This list contain recent elements for more than 50'000 asteroids.
You can carefully modify some default options in the file EXTRES.INI.
HEASARC SkyView
This panel gives you the possibility to directly obtain a sky image
corresponding to the current chart.
You have to be connected to the Internet before you can use this function.
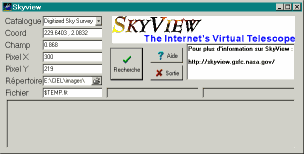
If you need more information on SkyView or if you which to obtain the
description of all available catalogs as well as the dimension limits,
please consult http://skyview.gsfc.nasa.gov
Do not modify the default value of "Coord" and "Field" if you want an
image for the current chart.
Otherwise you can give an object name in the field "Coord", which will
be resolved by SIMBAD.
The size of certain catalogs is limited (i.e. 4° in the case of
the DSS).
Pixel X et Pixel Y represent the number of pixel of the image. If these
two fields are empty, then the resolution of the catalog will be used.
Warning: keep an eye on the size of the file you are going to transfer!
If you plan to keep the file for later utilization, give a name to it in the corresponding field but do not modify the extension ".fit".
Estimation of the file size:
The data has a depth of 32 bit and the header is negligible.
The size in bytes is: : pixelx * pixely * 4 giving 360 KB for an image
of 300x300.